How to Fix the ‘Error Establishing a Database Connection’ in WordPress
The “Error Establishing a Database Connection” indicates WordPress cannot connect to the MySQL database, which stores all site content and settings. When this connection fails, WordPress is unable to display information, resulting in a complete site outage and a blank page with the error message displayed.
Typical Causes of Database Connection Errors
Here are the most frequent reasons for this error:
- Incorrect Database Credentials: An incorrect database name, username, or password in your configuration file can block access.
- Database Corruption: Plugins, server issues, or unexpected shutdowns can corrupt your database.
- Server Downtime: Hosting server issues, like traffic surges or server malfunctions, can temporarily prevent a database connection.
- Database Usage Limit Reached: Shared hosting plans may restrict database usage, which can cause issues under heavy traffic.
Step-by-Step Solutions for Fixing the Database Connection Error
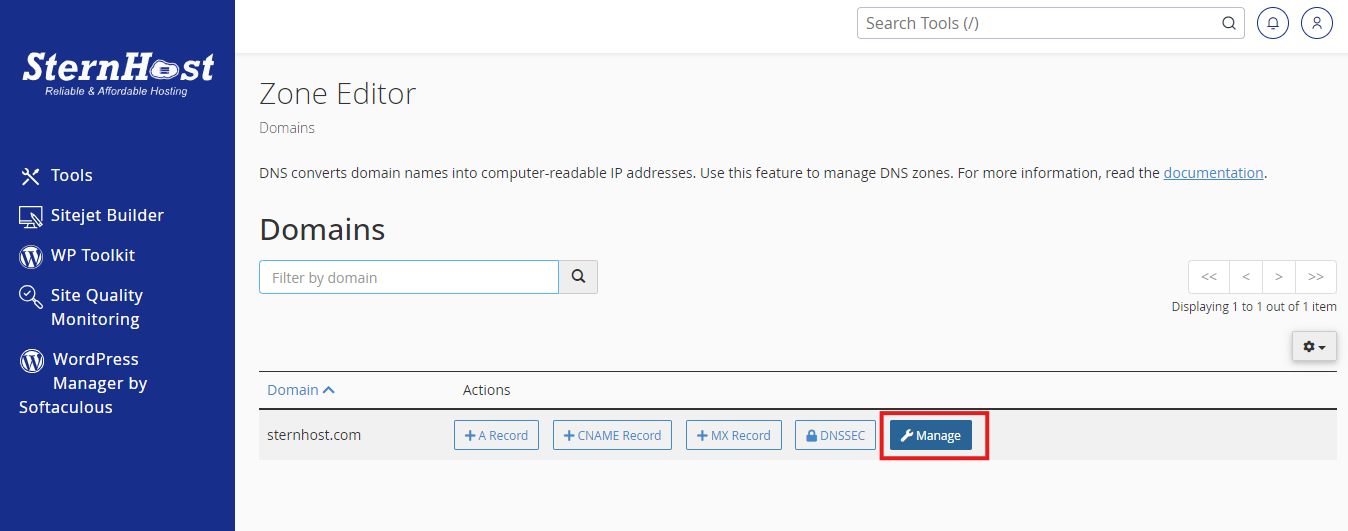
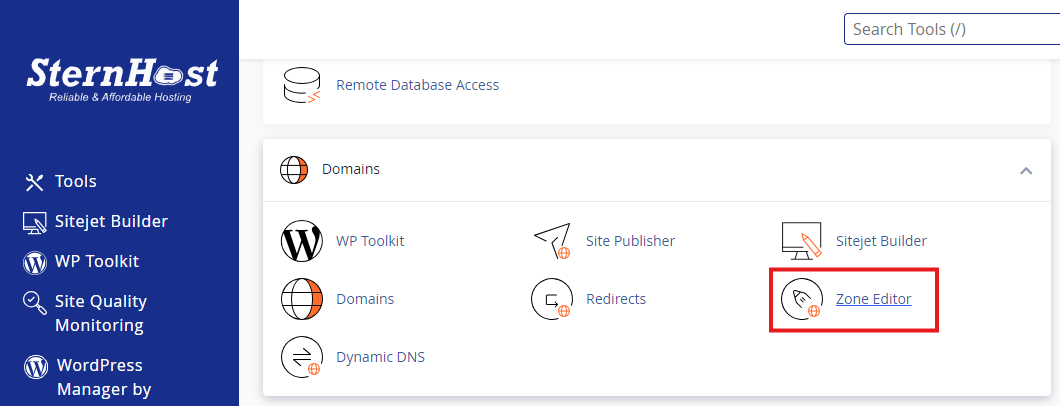
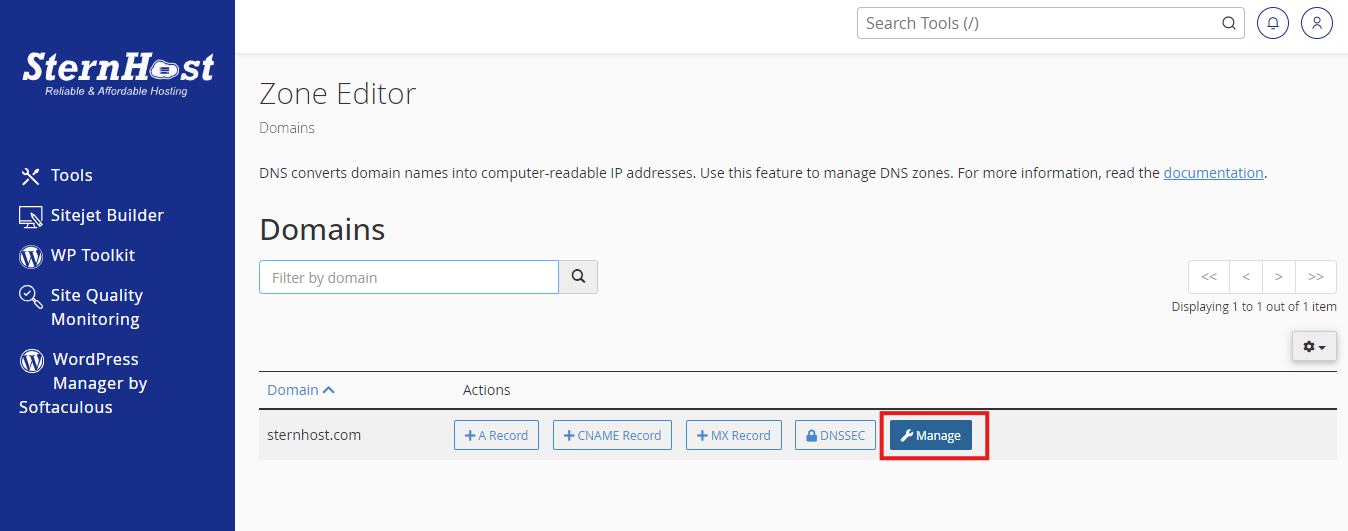
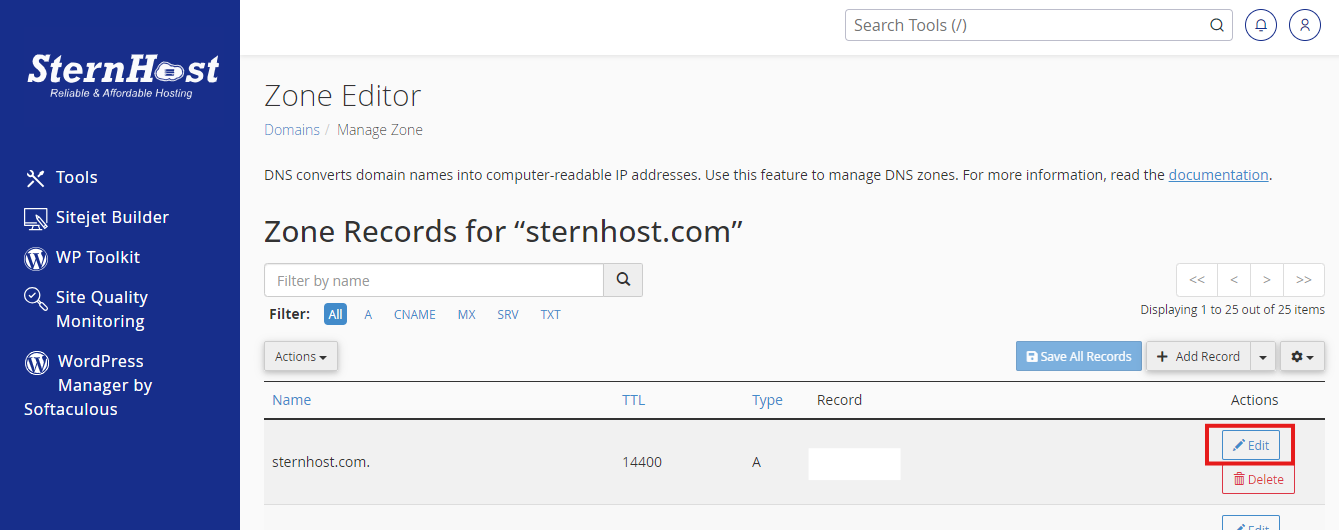
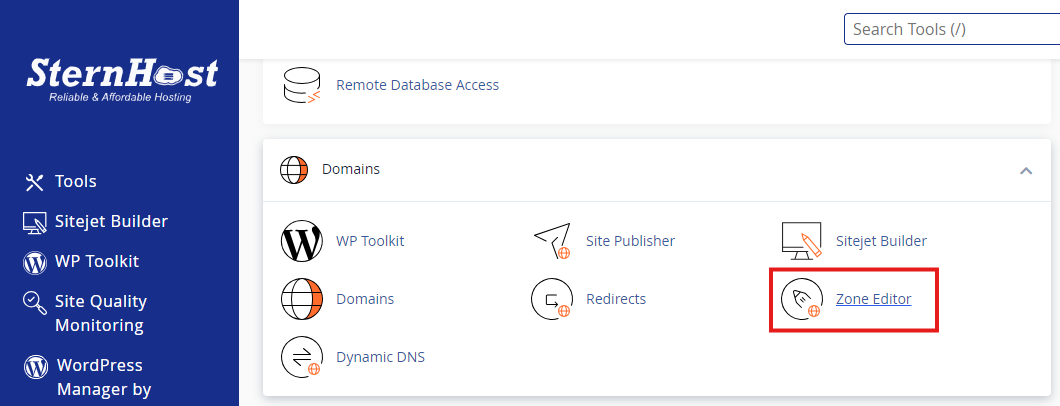
1. Verify Database Credentials in wp-config.php
Your WordPress configuration file, wp-config.php, contains essential database credentials. Here’s how to check them:
- Access wp-config.php: Use an FTP client or your hosting file manager to locate this file in your WordPress root directory.
- Confirm Credentials: Open the file and check these lines:
define('DB_NAME', 'your_database_name');
define('DB_USER', 'your_database_username');
define('DB_PASSWORD', 'your_database_password');
define('DB_HOST', 'localhost');
Update If Necessary: Make sure these values match those in your hosting account. If they don’t, update them, save the file, and reload your site.
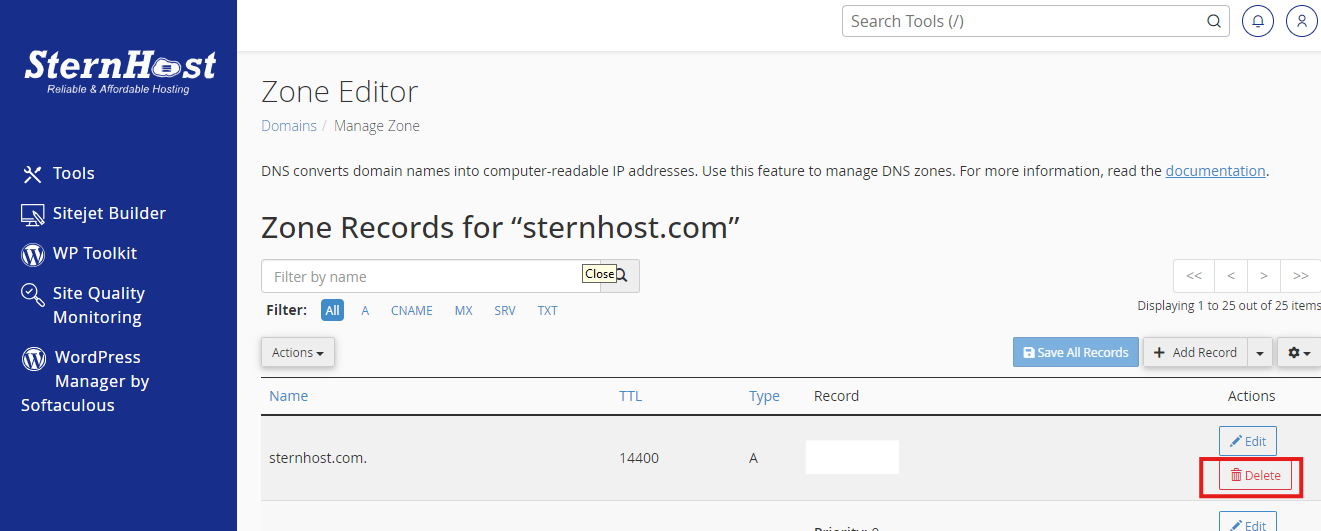
2. Repair a Corrupted Database
WordPress offers a built-in repair feature:
Enable Repair: Add this line to wp-config.php:define('WP_ALLOW_REPAIR', true);
- Run Database Repair: Visit http://yourwebsite.com/wp-admin/maint/repair.php and select “Repair Database.” Once complete, remove the repair line from wp-config.php for security.
3. Check Your Database Server (DB_HOST)
If issues persist, your database server may be down:
- Contact Hosting Support: Your hosting provider can confirm if the server is experiencing issues.
- Test Connection: Create a PHP file called testconnection.php with this code:
<?php
$link = mysqli_connect("localhost", "DB_USER", "DB_PASSWORD");
if (!$link) {
die("Database connection error: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
echo "Connected successfully!";
?>
Replace the placeholders with your database credentials and upload the file to your site’s root directory. Visit http://yourwebsite.com/testconnection.php to confirm connectivity.
4. Increase PHP Memory Limit
Low PHP memory can sometimes cause this error:
Increase Limit in wp-config.php: Add this line to your wp-config.php file:
define('WP_MEMORY_LIMIT', '256M');- Save and Upload: Upload the modified file to increase WordPress’s available resources.
5. Restore a Database Backup
If none of the steps above resolve the error:
- Access Backups in Hosting Panel: Locate the latest database backup and restore it.
- Backup Current Data: Ensure to create a backup of the current database for safekeeping.
6. Consult Your Hosting Provider
If all else fails, reach out to your hosting provider for additional support. They may need to review server configurations.
Preventing Future Database Connection Errors
To minimize the chance of this error recurring:
- Use a Reliable Hosting Provider: Ensure your hosting provider is reputable with reliable support.
- Schedule Regular Backups: Protect your data by making regular backups.
- Limit Resource-Heavy Plugins: Too many plugins can strain resources, so use only necessary ones.
- Ensure Compatibility: Keep your WordPress, plugins, and themes updated.
Conclusion
While the “Database Connection Error” can disrupt your site, these steps can help you restore functionality. Checking credentials, repairing the database, and seeking hosting support are effective ways to resolve the error. To prevent future issues, maintain regular backups, choose a reliable host, and monitor plugins for compatibility.
By choosing SternHost, you’re opting for premium domain registration, secure web hosting, and optimized WordPress hosting solutions designed for high performance and reliability.
Let SternHost handle the backend, so you can focus on delivering a flawless experience to your audience. Get started today and empower your website with SternHost











 2.
2.  3.
3.